- The Japanese Yen turns higher against a broadly weaker USD following an early Asian session slide.
- Hopes for an eventual US-Japan trade deal, BoJ rate hike bets and geopolitical risks underpin the JPY.
- US fiscal concerns and dovish Fed expectations weigh on the USD, exerting pressure on USD/JPY.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) hit a fresh monthly high against its American counterpart following an Asian session slide on Monday and seems poised to appreciate further. Hopes that Japan will strike a trade deal with the US soon and the growing acceptance that the Bank of Japan (BoJ) will continue raising interest rates turn out to be key factors acting as a tailwind for the JPY. Apart from this, rising geopolitical risks stemming from the protracted Russia-Ukraine war and conflicts in the Middle East further benefit the safe-haven JPY.
However, US President Donald Trump’s decision to delay the implementation of tariffs on the European Union (EU) is holding back the JPY bulls from placing fresh bets and lending some support to the USD/JPY pair. Any meaningful upside for the pair, however, still seems elusive in the wake of the prevalent US Dollar (USD) selling bias, fueled by concerns about US fiscal health. Moreover, expectations that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will lower borrowing costs weigh on the USD and should act as a tailwind for the lower-yielding JPY.
Japanese Yen might continue to benefit from hopes for a US-Japan trade-deal and BoJ rate hike bets
- Following a third round of Japan-US talks, Japan’s Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba said on Sunday that Tokyo aims to advance tariff talks with the US, with the goal of achieving an outcome during the Group of Seven summit next month. Moreover, Japan’s top tariff negotiator Ryosei Akazawa said that the schedule for the next Japan-US talks is being arranged and that he hopes to meet US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent during his next visit.
- Friday’s hotter-than-expected consumer inflation figures from Japan, along with expectations that higher wages will boost prices, keep the door open for further policy tightening by the Bank of Japan. In fact, BoJ officials recently showed a willingness to hike interest rates again if the economy and prices improve as projected. Investors, however, now seem convinced that policymakers will assess tariffs and trade flows before making the next move.
- On the geopolitical front, Russian forces launched a massive drone and missile attack across Ukrainian cities, marking the war’s largest aerial attack to date. Speaking to reporters, US President Donald Trump called the attack unacceptable and said that he was considering new sanctions against Russia. Meanwhile, Israeli strikes over the past 24 hours killed at least 38 people in Gaza, including children. Israel had said earlier that it plans to seize full control of Gaza.
- Trump’s sweeping tax cut and spending bill is expected to add around $4 trillion to the nation’s deficit over the next 10 years and swell the federal government’s debt. Moreover, traders have been pricing in the possibility that the Federal Reserve will lower borrowing costs further this year. This, in turn, drags the US Dollar to a nearly one-month low and also benefits the lower-yielding JPY, which, in turn, supports prospects for a further USD/JPY depreciation.
- The focus now shifts to this week’s important US macro releases – Durable Goods Order on Wednesday, followed by the Prelim GDP print and the Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) Price Index on Thursday and Friday, respectively. Apart from this, the FOMC meeting minutes on Wednesday will play a key role in influencing the USD price dynamics, which, along with Tokyo CPI on Friday, should provide some meaningful impetus to the USD/JPY pair.
USD/JPY bearish technical setup supports prospects for an extension of a one-week-old downtrend
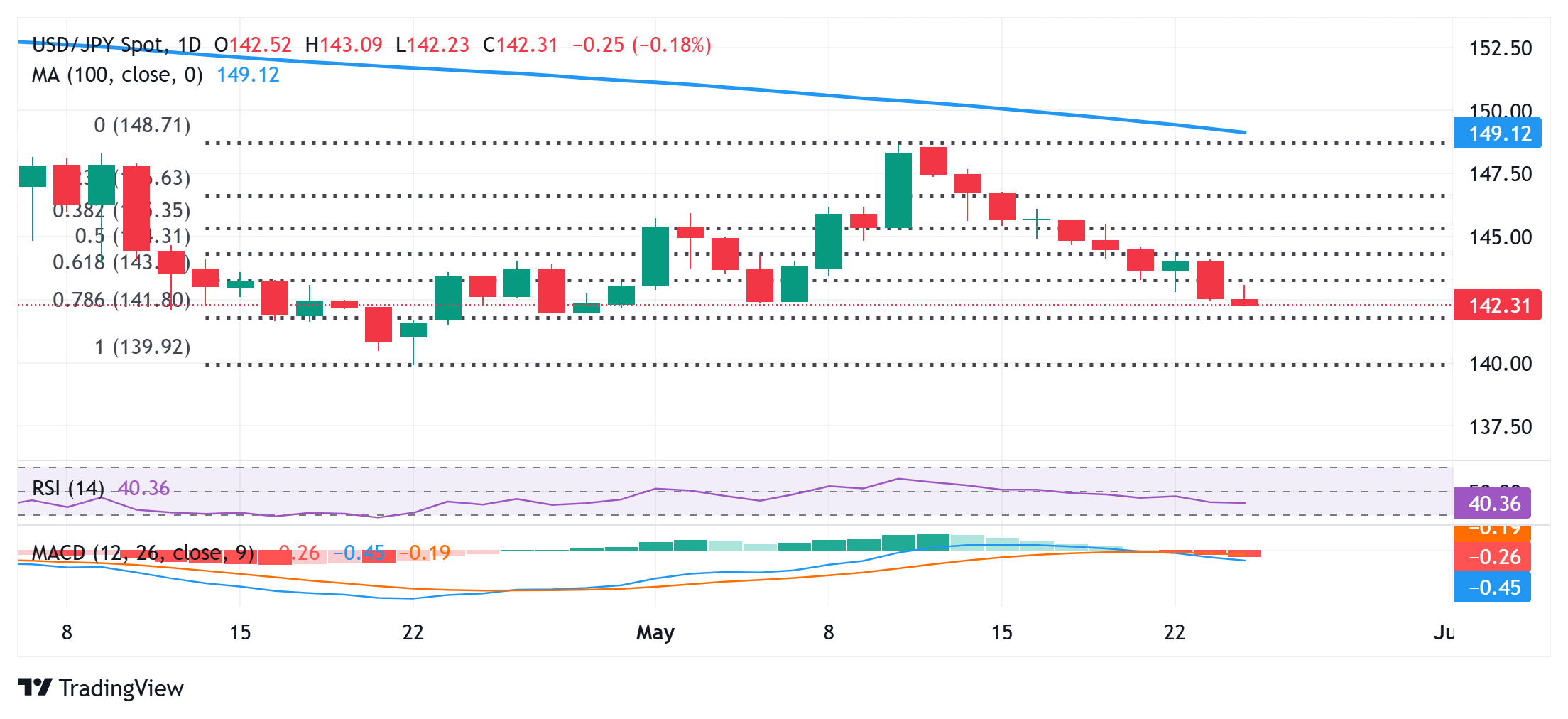
From a technical perspective, an intraday failure near the 143.00 round-figure mark validates last week’s breakdown below the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level of April-May move higher. Adding to this, oscillators on the daily chart have been gaining negative traction and suggest that the path of least resistance for the USD/JPY pair remains to the downside. Some follow-through selling below the 142.00 mark will reaffirm the bearish outlook and drag spot prices below the 141.55 intermediate support, towards the 141.00 round figure. The subsequent downfall would expose the year-to-date low, or levels below the 140.00 psychological mark touched on April 22.
On the flip side, the Asian session peak, around the 143.10 area, now seems to act as an immediate hurdle, above which a bout of a short-covering move could lift the USD/JPY pair to the 143.65 region en route to the 144.00 round figure. The latter should act as a strong barrier, which, if cleared, could pave the way for a further recovery. However, the move higher might still be seen as a selling opportunity near the 144.80 zone and remain capped near the 145.00 psychological mark.
Bank of Japan FAQs
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) is the Japanese central bank, which sets monetary policy in the country. Its mandate is to issue banknotes and carry out currency and monetary control to ensure price stability, which means an inflation target of around 2%.
The Bank of Japan embarked in an ultra-loose monetary policy in 2013 in order to stimulate the economy and fuel inflation amid a low-inflationary environment. The bank’s policy is based on Quantitative and Qualitative Easing (QQE), or printing notes to buy assets such as government or corporate bonds to provide liquidity. In 2016, the bank doubled down on its strategy and further loosened policy by first introducing negative interest rates and then directly controlling the yield of its 10-year government bonds. In March 2024, the BoJ lifted interest rates, effectively retreating from the ultra-loose monetary policy stance.
The Bank’s massive stimulus caused the Yen to depreciate against its main currency peers. This process exacerbated in 2022 and 2023 due to an increasing policy divergence between the Bank of Japan and other main central banks, which opted to increase interest rates sharply to fight decades-high levels of inflation. The BoJ’s policy led to a widening differential with other currencies, dragging down the value of the Yen. This trend partly reversed in 2024, when the BoJ decided to abandon its ultra-loose policy stance.
A weaker Yen and the spike in global energy prices led to an increase in Japanese inflation, which exceeded the BoJ’s 2% target. The prospect of rising salaries in the country – a key element fuelling inflation – also contributed to the move.


